Nmap
Host Discovery
Scan Type Example Command
ARP Scan
sudo nmap -PR -sn MACHINE_IP/24ICMP Echo Scan
sudo nmap -PE -sn MACHINE_IP/24ICMP Timestamp Scan
sudo nmap -PP -sn MACHINE_IP/24ICMP Address Mask Scan
sudo nmap -PM -sn MACHINE_IP/24TCP SYN Ping Scan
sudo nmap -PS22,80,443 -sn MACHINE_IP/30TCP ACK Ping Scan
sudo nmap -PA22,80,443 -sn MACHINE_IP/30UDP Ping Scan
sudo nmap -PU53,161,162 -sn MACHINE_IP/30Remember to add
-snif you are only interested in host discovery without port-scanning. Omitting-snwill let Nmap default to port-scanning the live hosts.Target from file:
-iL hosts.lst— read target IPs/hosts from file (one per line).IP range in one octet:
10.129.2.18-20— same as 10.129.2.18, 10.129.2.19, 10.129.2.20.
Option Purpose
-nno DNS lookup-Rreverse-DNS lookup for all hosts-snhost discovery only-Pnskip host discovery (treat all hosts as up; use when target blocks ping or for reliable HTB/VPN scans)--disable-arp-pinguse ICMP (or other) instead of ARP for host discovery when on same L2--packet-traceshow all packets sent and received (useful for understanding scan behavior)--reasonshow why a port/host is in a given state (e.g. syn-ack, arp-response)
Port Scan Type Example Command
TCP Connect Scan
nmap -sT MACHINE_IPCompletes the full TCP 3-way handshake (SYN → SYN-ACK → ACK). Most accurate — gives definitive open/closed/filtered. Creates connection logs on the target so less stealthy, but behaves like a normal client so it is less likely to crash services. Used when Nmap does not have raw packet privileges (non-root).
TCP SYN Scan
sudo nmap -sS MACHINE_IPSends SYN, never completes the handshake. SYN-ACK back = open, RST back = closed, no response = filtered. Default scan when running as root. Stealthier than
-sTbecause no full connection is established, minimizing log entries — though modern IDS can still detect it.
UDP Scan
sudo nmap -sU MACHINE_IPStateless — no handshake. Nmap sends empty datagrams; no response = open|filtered, ICMP port unreachable = closed, application response = open. Much slower than TCP scans due to longer timeouts.
Option Purpose
-p-all ports-p1-1023scan ports 1 to 1023-p 22,25,80,139,445comma-separated specific ports--top-ports=10scan the N most common ports from Nmap's database (default scans top 1000)-F100 most common ports-rscan ports in consecutive order-T<0-5>timing templates:-T0paranoid /-T1sneaky /-T2polite /-T3normal (default) /-T4aggressive /-T5insaneToo aggressive (
-T5) can miss ports on congested networks or trigger IPS blocks
--max-rate 50rate <= 50 packets/sec--min-rate 15rate >= 15 packets/sec--min-parallelism 100at least 100 probes in parallel--max-retries 0fewer retries = faster scan, may miss ports (default 10).--initial-rtt-timeout 50ms --max-rtt-timeout 100msspeed up by lowering RTT timeouts; too low can miss hosts/ports.--stats-every=5sprint scan progress every 5s (or5m). During a scan, press Space to show current status.
Nmap Results
Open: indicates that a service is listening on the specified port.Closed: indicates that no service is listening on the specified port, although the port is accessible. By accessible, we mean that it is reachable and is not blocked by a firewall or other security appliances/programs.Filtered: Nmap cannot determine open or closed. Dropped = no response (retries up to--max-retries). Rejected = target sends e.g. ICMP type 3 code 3 (port unreachable).Unfiltered: port accessible but open/closed unknown; occurs with ACK scan (-sA). ACK scan often bypasses firewalls that block SYN/Connect.Open|Filtered: no response (common for UDP).Closed|Filtered: only in IP ID idle scan.UDP: Closed = ICMP port unreachable (type 3/code 3). No response = open|filtered. Application response = open.
Nmap Advanced Scanning
Port Scan Type Example Command
TCP Null Scan
sudo nmap -sN MACHINE_IPTCP FIN Scan
sudo nmap -sF MACHINE_IPTCP Xmas Scan
sudo nmap -sX MACHINE_IPThree above scan types can be efficient when scanning a target behind a stateless (non-stateful) firewall. A stateless firewall will check if the incoming packet has the SYN flag set to detect a connection attempt. Using a flag combination that does not match the SYN packet makes it possible to deceive the firewall and reach the system behind it.
TCP Maimon Scan
sudo nmap -sM MACHINE_IPTCP ACK Scan
sudo nmap -sA MACHINE_IPTCP Window Scan
sudo nmap -sW MACHINE_IPCustom TCP Scan
sudo nmap --scanflags URGACKPSHRSTSYNFIN MACHINE_IPSpoofed Source IP
sudo nmap -S SPOOFED_IP MACHINE_IPSpoofed MAC Address
--spoof-mac SPOOFED_MACDecoy Scan
nmap -D DECOY_IP,ME MACHINE_IPIdle (Zombie) Scan
sudo nmap -sI ZOMBIE_IP MACHINE_IPFragment IP data into 8 bytes
-fFragment IP data into 16 bytes
-ff
Advanced Options
--source-port PORT_NUMspecify source port number--data-length NUMappend random data to reach given length-vverbose (shows open ports as discovered)-vvvery verbose-ddebugging-ddmore details for debuggingNull, FIN, and Xmas scans provoke a response from closed ports. Maimon, ACK, and Window scans provoke a response from open and closed ports.
Subnet enumeration
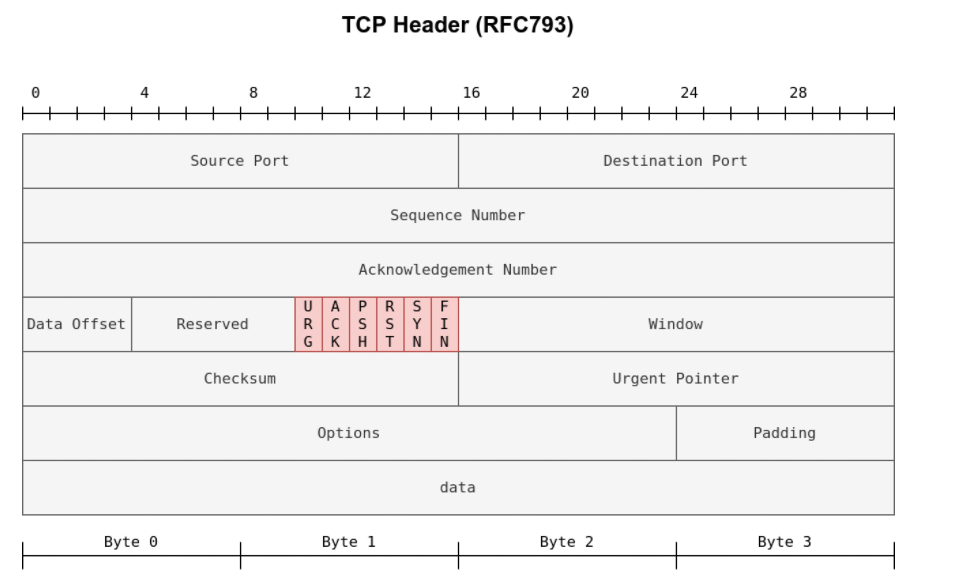
TCP Header
NSE
Script Category Description
authAuthentication related scriptsbroadcastDiscover hosts by sending broadcast messagesbrutePerforms brute-force password auditing against loginsdefaultDefault scripts, same as -sCdiscoveryRetrieve accessible information, such as database tables and DNS namesdosDetects servers vulnerable to Denial of Service (DoS)exploitAttempts to exploit various vulnerable servicesexternalChecks using a third-party service, such as Geoplugin and VirustotalfuzzerLaunch fuzzing attacksintrusiveIntrusive scripts such as brute-force attacks and exploitationmalwareScans for backdoorssafeSafe scripts that won’t crash the targetversionRetrieve service versionsvulnChecks for vulnerabilities or exploit vulnerable services
Run Scripts
--script banner,smtp-commandsgrabs the service banner and enumerates SMTP commands — useful for identifying OS/distro from the SMTP greeting.--script vulnruns all vuln-category scripts against the target; combine with-sVso scripts have version info to match against CVE databases.
NSE + Output
Option Meaning
-sVdetermine service/version info on open ports-sV --version-lighttry the most likely probes (2)-sV --version-alltry all available probes (9)If
-sVtruncates the banner, use manualnc+tcpdumpto capture the full banner (see Banner Grabbing).-Odetect OS--tracerouterun traceroute to target--script=SCRIPTSNmap scripts to run-sCor--script=defaultrun default scripts-Aequivalent to -sV -O -sC --traceroute-oNsave output in normal format-oGsave output in grepable format-oXsave output in XML format-oAsave output in normal, XML and Grepable formatsHTML report:
xsltproc target.xml -o target.html— convert XML to readable HTML for reporting.
Quick / full scan pattern
Searching Through Output
Looking for open port 445 in nmap output and returning ips
Firewall and IDS/IPS Evasion
ACK Scan for Firewall Detection
-sAsends only the ACK flag. Firewalls often allow ACK packets through because they cannot tell whether the connection was initiated internally or externally — ACK looks like part of an established session.Result: unfiltered (RST received — port is accessible through the firewall) or filtered (no response / ICMP error — firewall is blocking).
ACK scan does not distinguish open from closed — it only reveals firewall rules.
Decoy Scan
-D RND:5generates 5 random source IPs and mixes your real IP among them, making it harder to identify the true scanner in logs.Decoy IPs must be alive hosts; otherwise SYN-flood protections may drop all traffic.
Source IP and Interface Spoofing
-S 10.129.2.200sets the source IP — useful for testing whether a different subnet bypasses firewall rules.-e tun0forces Nmap to send through a specific network interface (required when spoofing source IP).
DNS Source Port Evasion
Firewalls often trust traffic from
TCP/UDP port 53(DNS). Using--source-port 53can bypass poorly configured firewalls.--dns-server <ns>,<ns>lets you specify custom DNS servers — useful in a DMZ where the company's internal DNS is more trusted.
Once you confirm source port 53 bypasses the firewall, connect directly with ncat:
Last updated